Data skipping is a crucial performance optimization technique, especially in OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) environments. One of the most effective ways to enable data skipping is through partitioning — a technique widely used in lake house architecture or any other storage.
Key principle
Instead of scanning the entire dataset in a table, data skipping allows the system to bypass irrelevant data and focus only on the specific records or files needed to answer a query. This dramatically reduces the amount of data read from storage and speeds up query execution.
In partitioning, data is physically divided into separate folders or files based on a chosen column (called the partition key).
For instance, consider an e-commerce platform with billions of sales records. If the data is partitioned by year, then when you query sales from a specific year, the system only needs to look inside that year’s folder — skipping all other folders. This targeted access saves both time and computing resources. Below is the sample image of how data stored in storage location.

Choosing the Right Partition Key
Partitioning works best when queries frequently filter or join on specific columns. Typically, low-cardinality columns (columns with fewer unique values) make good partition keys — such as year, region, or category.
Choosing the right key ensures queries can quickly zero in on the relevant data without scanning the entire dataset.
Implementation
While writing, use the partitionBy method and mention the field to partition by.

Below is the data stored in Azure data lake storage.

Experiment
Below is the search query and Spark execution plan.
The query fetches records that belong to May 2025 and where the temperature is above 40˚C. Since the query filters on year and month, and the data is already partitioned by these fields, Spark scans only the relevant partitions. As a result, it reads less than 1% of the total data to produce the result.


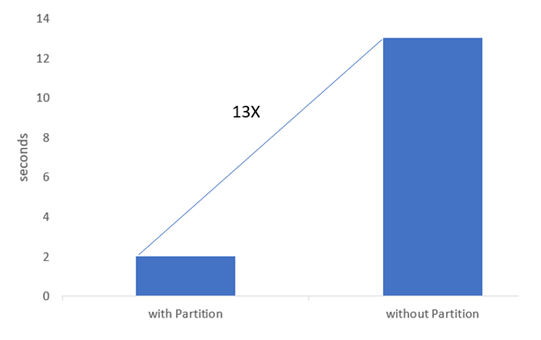
Below is a comparison of running the same query on two tables — one without partitioning and another with partitioning. The performance difference is massive. This clearly demonstrates why partitioning is one of the key techniques that make data skipping so powerful.
Cons of hive style partitioning
- It can make worse small file problem.
- Not suitable to partition by high cardinality columns.
Conclusion
Data skipping combined with effective partitioning can significantly improve query performance by reducing data scans and computation time. However, careful selection of partition keys is essential to avoid issues like small file proliferation. When designed well, partitioning becomes a powerful enabler of fast, efficient analytics in OLAP systems.
References
Leave a comment