Parameterization is one of the important best practise activities in data pipeline design like any system designing to keep the code clean and easy maintainable.
Parameterizing linked services in Azure Data Factory is crucial for reusability and flexibility across different environments or functions It enables dynamic connections by allowing values like server names, database names, or keys to be passed at runtime. This reduces duplication and improves maintainability of the pipeline infrastructure.
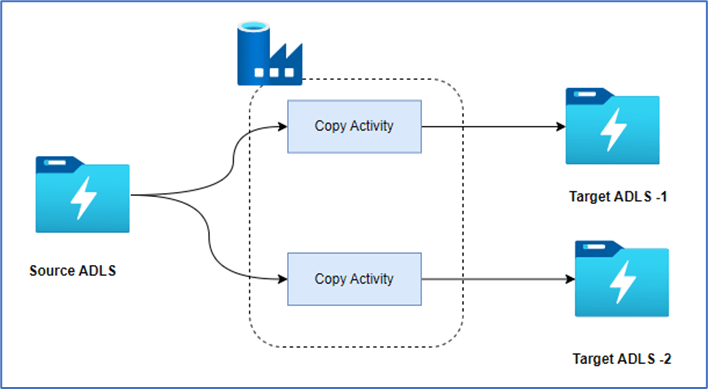
Let’s try to copy csv file from ADLS location and across load into multiple locations using single linked service.
The below repo has the code of this demo and root folder is adf_ls_param.
https://github.com/ArulrajGopal/kaninipro/tree/main/adf_ls_param

Infrastructure setup
- use ls_param/helper/terraform/main.tf as terraform code to setup all storage account, data-factory and service principal with appropriate access
- run helper/copy_sample_data_storage.py to prepare the sample data, which actually copy the sample data from public storage account to source ADLS
Azure Resources will be created.
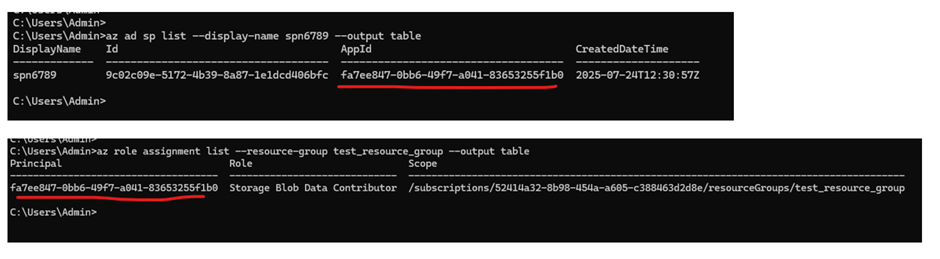
Service principal created with access to storage account at resource group level. (this screenshot take using azure cli login)
Pipeline setup walkthrough
After the code deployed into the Azure data factory, the below pipeline, linked-service and datasets are available.
Copy activities in pipeline
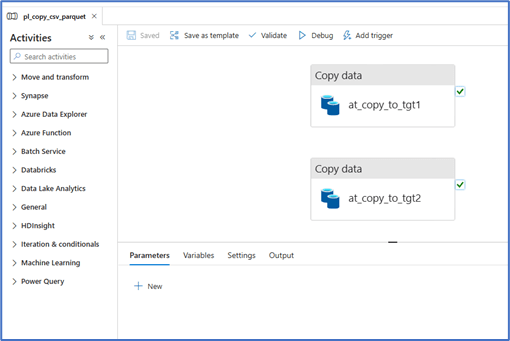
The Copy activity copies data from the source ADLS using the source dataset and target dataset where both are connected to single ADLS linked service.
Linked Service
The below is the parameterized linked service in json format. URL is formed throuh parameter passed to the linked service.

Note: –
- All the storage account which to be accessed using the linked service should able to accessed by single service principle to make the process easier and easy maintainable.
- In real-time projects, the service-principle secret passed through key vault to make it secure. For this demo sake, service-principle key hardcoded and it need to be done manually git integrated.
- Id’s are masked in the json code.
Source Dataset

Target Dataset (parameterized with storage account name)
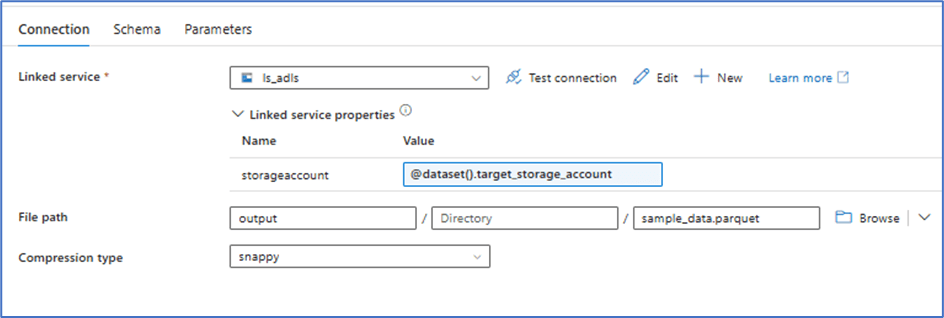
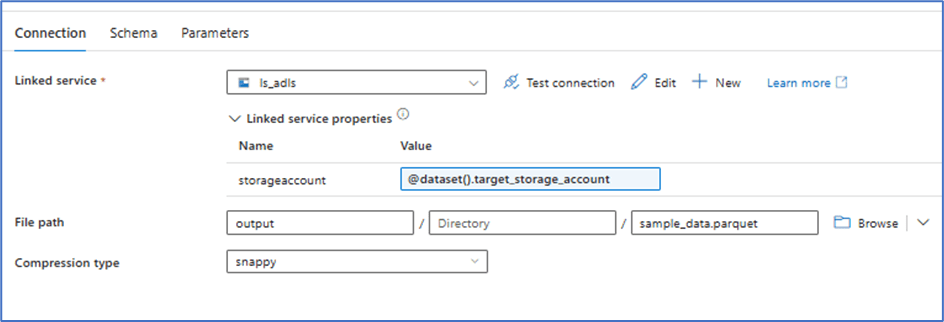
Execution
With this setup, the process can using single linked service.

Data copied from source to target
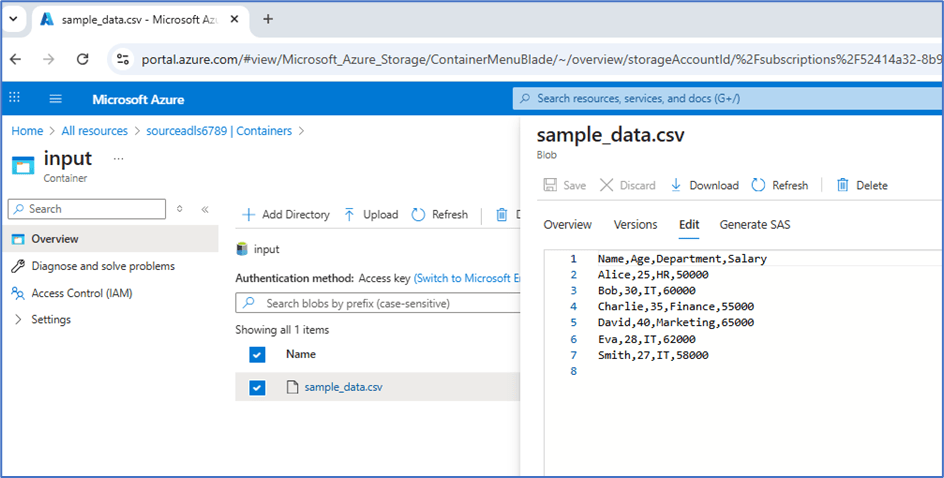
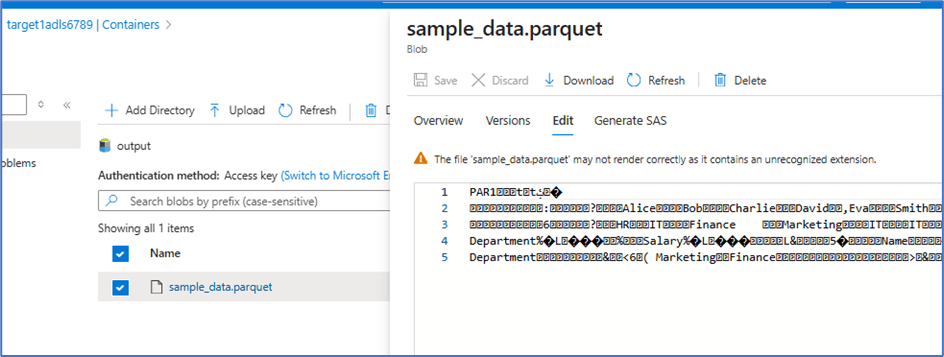
Conclusion
The solution efficiently copies a CSV file from ADLS and converts it into Parquet files, storing them in two separate ADLS instances using a single ADLS linked service.
This approach ensures efficient data transformation and maintains security best practices by leveraging Azure’s built-in tools for seamless data handling across multiple storage instances.
If the two ADLS instances require access through different Azure IDs instead of a shared service principle, using managed identities is the optimal solution. Managed identities enhance security by eliminating the need to manage credentials, offering a more streamlined and secure authentication mechanism.
Leave a comment