Removing duplicates in any data processing systems is essential, like other systems spark has some good ways to get rid of duplicates. We will look into the different ways of removing duplicates spark and application of that.
- distinct
- drop duplicates
- group by
- windows functions
Distinct & Drop duplicates.
Distinct and drop duplicates are most common ways and used to remove the duplicates (meaning out of duplicates it will retain one record and remove others).
Distinct don’t need any parameters it will remove the duplicate record based on all columns, whereas in drop duplicates can remove the duplicates based on the subset of the columns. In case of no columns provided, drop duplicates will act as distinct.
Example dataset: –

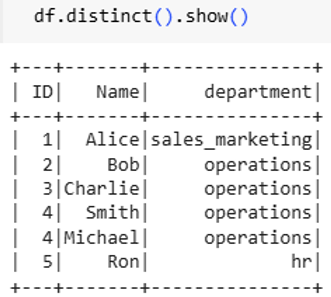
Result of distinct: –
Result of drop duplicates with and without key: –

Drop duplicate will faster and efficient in case of keys provided, because deduplication in fewer columns.
Caveat of drop duplicates – While deduping the records using drop duplicates, and multiple rows have the same values in keys, spark will keep the first occurrence it encounters and drop the rest.
How does spark decides which one is first? – Spark does not guarantee a consistent order unless you explicitly sort the DataFrame before using drop duplicates. The “first” row is determined by underlying data partitioning and execution plan, which may vary between runs, which will lead to inconsistent data flow to downstream.
The example for same dataset and operation returns different result.

To avoid this, it is recommended to use ORDER BY followed by DROP DUPLICATES, or consider alternative approaches listed below.
Windows functions
Using window functions along with ranking or row numbering the duplicate can be removed. The below code removes duplicates and has higher control of which record to be eliminated by specifying the field in order by (mostly it will be time related field).
This method gives the Deterministic Output, but not ideal for simple deduplication.

Group by
At some situations, dedupe the dataset by get rid of all instances of duplicate records. For example, as shown below remove the duplicates and don’t retain any one of instances which is repeated.

This logic is applied in scenarios where the workflow cannot determine which record should be eliminated. In such cases, both records are removed, logged to a specified path, and a notification is sent to the downstream system for further investigation. This can be achieved using the code below.

An important factor to note is that this approach involves two wide transformations in spark—groupBy and join—which can have a significant impact on performance.
In conclusion, Spark provides several effective techniques for removing duplicates, including distinct, dropDuplicates, window functions, and groupBy. Choosing the most appropriate method based on the context not only ensures accuracy but also enhances system performance and efficiency.
Keep Learning !! Happy Engineering !!!
Leave a comment